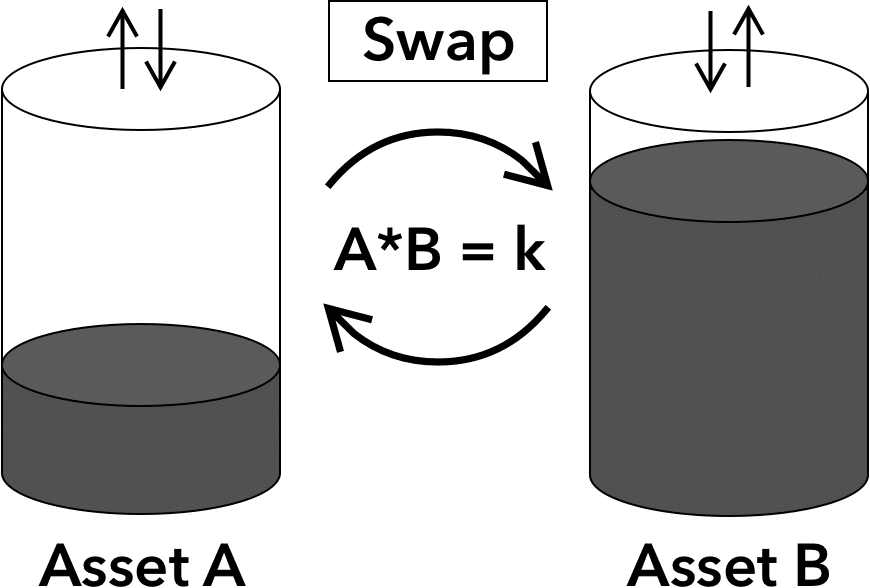
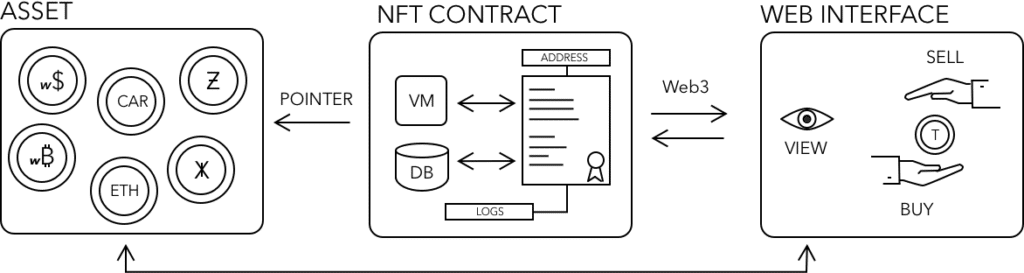
A Decentralized Exchange (DEX) is a service that allows participants to list and exchange assets directly and openly. DEXs are implemented on-chain using smart-contracts. Using these decentralized applications (DApps) it is possible to list, buy, and sell any type of asset, including cryptocurrencies, stocks, or any other type of securities.
Exchanges can be broadly classified into two categories:
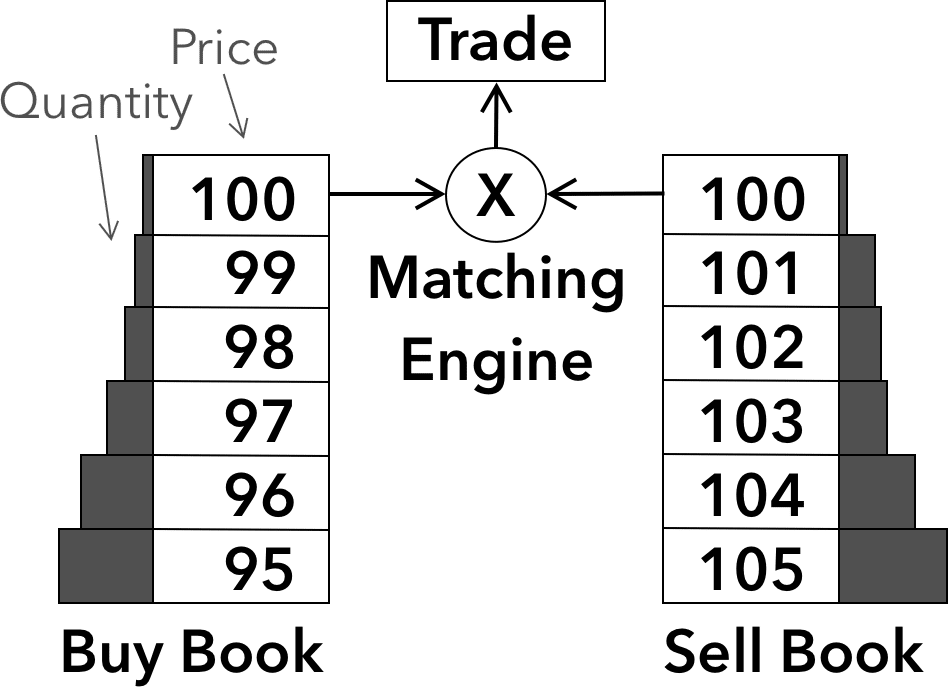
- Order book exchanges: An order book exchange is a type of exchange that operates by matching buyers and sellers based on their orders. Buyers place orders to buy an asset at a specific price, and sellers place orders to sell an asset at a specific price. The exchange matches the orders and executes the trade when the bid and ask prices cross (i.e., a buyer is willing to pay at least the same price as a seller is willing to sell). Examples of order book exchanges include traditional stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase and Binance.
- Automated Market Makers (AMMs): Automated Market Makers are a type of exchange that operates using algorithms to automatically set the prices of assets based on supply and demand. AMMs do not use an order book to match buyers and sellers. Instead, they use a simple algorithm to calculate the price of an asset based on the amount of it that is being bought and sold. Examples of AMMs include UniSwap and SushiSwap in the cryptocurrency space.